What is a Johari window?
The Johari Window is a psychological tool used for understanding and improving self-awareness, interpersonal relationships, and communication. It was created by psychologists Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham in 1955, and its name is a combination of their first names.
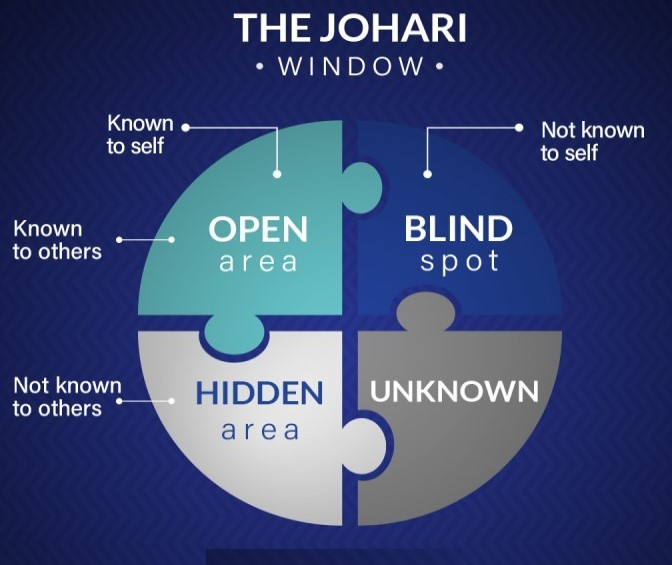
The Johari Window is represented as a four-quadrant grid:
- Open Area (Arena):
This quadrant contains information that is known both to you and others. It includes things like your behavior, skills, and attitudes that you openly share and others recognize. - Blind Spot:
This quadrant consists of things about you that others know, but you are unaware of. For example, habits or traits you might not notice about yourself, but others see. - Hidden Area (Façade):
This area includes things you know about yourself but choose to keep hidden from others, such as personal secrets, insecurities, or private information. - Unknown Area:
This quadrant contains information that neither you nor others are aware of. It represents untapped potential, hidden talents, or unconscious aspects of your personality.
The goal of the Johari Window is to expand the Open Area by improving self-disclosure and seeking feedback, which can enhance trust and communication in relationships
What is used for ?
The Johari Window is used primarily for self-awareness, personal growth, and improving communication within groups or relationships. Its applications include:
- Self-awareness and Personal Development:
It helps individuals understand themselves better by revealing their blind spots through feedback from others. This can lead to improved emotional intelligence, self-reflection, and greater confidence. - Improving Communication:
By encouraging open communication, it fosters a better understanding between individuals or team members, reducing misunderstandings and enhancing collaboration. - Building Trust:
It encourages sharing personal thoughts, feelings, and experiences (from the Hidden Area to the Open Area), which promotes vulnerability and trust within relationships or teams. - Team Building:
In group settings, the Johari Window is used to improve team dynamics. It helps members learn more about each other’s strengths, weaknesses, and communication styles, leading to stronger cooperation and effectiveness. - Conflict Resolution:
By making hidden or misunderstood aspects more transparent, it helps resolve conflicts caused by miscommunication or lack of awareness.
Overall, the Johari Window is used to promote healthier, more effective interactions between people, improving both individual and group performance.